
The incident wave front is spherical is cylindrical. No lenses are used to make the light beam parallel and convergent. In this type of diffraction, screen and the source or both are at the finite distance from the obstacle or aperture. The incident wavefront is plane wavefrontDiffraction at diffraction grating, singleslit, etc are the examples of fraunhofer diffraction.

Lenses are used one to focus the light coming from infinity to the aperture and other to focus the diffracted light on the screen. In this type of diffraction, screen and source or both are at infinite distance from the obstacle or aperture.

DIFFRACTION PHYSICS SERIES
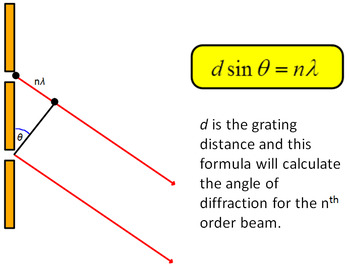
Diffraction is caused when the wave encounters with the diffracting object which is explained by Huygens Fresnel principle and principle of the superposition of waves which consider every particle on a wavefront as point source for the secondary wave and the displacement at any subsequent point is the sum of these secondary waves andalsothe amplitude being the sum of amplitude of the individual wave varying from zero to sum of individual amplitude giving series of maxima and minima. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Erik Gregersen.The process of bending of light around the edge of an aperture or obstacle is called diffraction of light. See also Bragg law Laue diffraction pattern. By observing the interference pattern, the internal structure of the crystal can be deduced. This leads to the Bragg law nλ = 2 d sin θ. To interfere constructively, the difference in path length between the beams reflecting off two atomic planes must be a whole number ( n) of wavelengths (λ), or nλ. The X-rays reflecting off two different planes must interfere constructively to form an interference pattern otherwise, the X-rays would interfere destructively and form no pattern. The X-rays reflect off atomic planes in the crystal that are a distance d apart.

It is reflected off the atoms of the crystal with the same angle θ. A beam of X-rays contacts a crystal with an angle of incidence θ. The atomic planes of the crystal act on the X-rays in exactly the same manner as does a uniformly ruled diffraction grating on a beam of light. X-ray diffraction, phenomenon in which the atoms of a crystal, by virtue of their uniform spacing, cause an interference pattern of the waves present in an incident beam of X-rays. SpaceNext50 Britannica presents SpaceNext50, From the race to the Moon to space stewardship, we explore a wide range of subjects that feed our curiosity about space!.Learn about the major environmental problems facing our planet and what can be done about them! Saving Earth Britannica Presents Earth’s To-Do List for the 21st Century.
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS HOW TO


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
